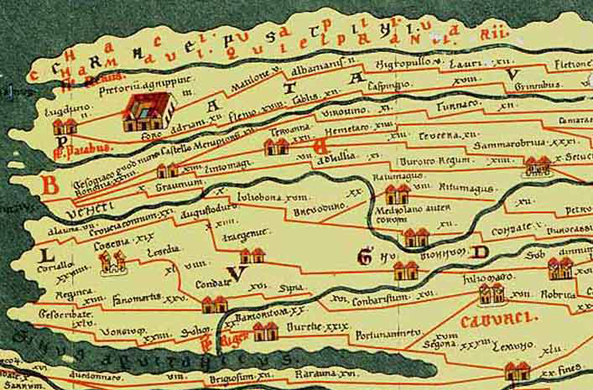
R O M A N - T I M E L I N E
23 The Senate grants Augustus the titles and powers of Imperium proconsulare maius and tribunicia potestas for life, thereby turning over to him complete control of the State and ending the Roman Republic
21-19 Without bloodshed Augustus wins back from King Phraates IV the Roman standards lost to the Parthians in 53
17 Secular Games (Ludi saeculares) celebrated as symbol of the new Golden Age brought in by Augustus
15 The territory of the Raeti and Celtic Vincelici (Tyrol,Bavaria,Switzerland) subdued, the new province of Raetia
instituted
13 July 4, consecration ceremony of the Altar of Peace (ara Pacis) voted by the Senate to honor Augustus
12 Augustus takes title and position of Pontifex Maximus
13-9 Campaigns in Pannoia
12-9 Campaigns in Germany
9 30 January, dedication of the completed Ara Pacis Augustae
5 Gaius Caesar, grandson of Augustus, named heir presumptive, princeps juventutis
4 most likely date for Birth of Jesus Christ
2 Augustus is awarded the honourific title of pater patriae. Lucius Caesar, brother of Gaius, likewise is name Princeps juventutis
--- AD ---
2 Lucius Caesar dies in Massilia
4 Gaius Caesar dies in Lycia from a wound sustained in battle eighteen months earlier
6-9 Pannonian revolt suppressed by Tiberius
9 Roman army under Varus suffers overwhelming defeat in the Teutoburg Forest in campaign against the Cherusci
14 August 19, Augustus dies at Nola. On September 17 the Senate elevates him to the pantheon of State gods,
an honor he had himself prepared by building a temple to the Divius Julius
14-37 Tiberius emperor
14-16 Germanicus, nephew and adopted heir of Tiberius leads campaign in Germany.
Germans evacuated to the right bank of the Rhine
19 Mysterious death (by poison?) of Germanicus in Antioch
21-22 The Praetorian Guard in Rome is concentrated into a single huge barracks (the Castra Praetoria),
a move engineered by their prefect Sejanus to make them into a political force
26 Tiberius saved by Sejanus when his grotto-villa at Sperlonga caves in. The emperor, rarely in the capital,
retires to Capri
26-31 Sejanus becomes all-powerful in Rome but is arrested and executed on October 18, AD 31
37 March March 16, death of Tiberius
37-41 Caligula emperor
39-40 To justify his military pretensions Caligula launches an abortive campaign against Germany and Britain
41 January 24, Caligula, his wife, and his only child are murdered
41-54 Claudius emperor
43-44 Britain brought under Roman rule
54-68 Claudius posisoned by his wife Agrippina, Nero emperor
62 Earthquake at Pompeii and nearby Vesuvian towns
64 Great fire in Rome. Persecution of Christians
65 Conspiracy against Nero by C. Calpurnius Piso is exposed and the plotters, among them Seneca and his nephew Lucan, executed
67 Nero in Greece
68 With revolts blazing in Gaul, Spain, and Africa as well as among the Praetorian Guard in Rome,
Nero flees and commits suicide
68-69 First crisis of the Empire: year of the Four Emperors Galba, Otho, Vitallius, Vespasian. On July 1, AD 69, Vespasian is proclaimed emperor but almost six months pass before he can eliminate rivals and enter Rome
69-79 Vespasian emperor, initiating Flavian dynasty
70 Titus, elder son of Vespasian, takes Jerusalem and destroys the Temple
79-81 Titus, co-regent since 71, sole ruler after death of his father in 79
79 August 24, eruption of Vesuvius buries Pompeii, Heraculaneum, and Stabiae
80 Great fire in Rome
81-96 Domitian, younger son of Vespasian, emperor
83-85 Campaigns against the Chatti in western Germany; building of border fortifications (limesin Germany
86-90 Difficulties with the Dacians settled by making King Decebalus a client-ruler
95 Expulsion of philosophers from Italy
96 Nerva emperor upon assassination of Domitian
|